What is electic charge and the SI unit of electric charge coulomb
What is electric charge?
Charge is one of a basic property of matter similar to mass or temperature. Charge is responsible for all electric and magnetic interactions of the matter. There are two flavors of charge, Positive (+) and Negative (-). In an atom, two sub-atomic particles protons and electrons are the charge carrying particles.
In an atom, protons in the atomic nucleus are positively charged particle and electrons in atomic orbitals (around the atomic nucleus) are the negatively charged particles.
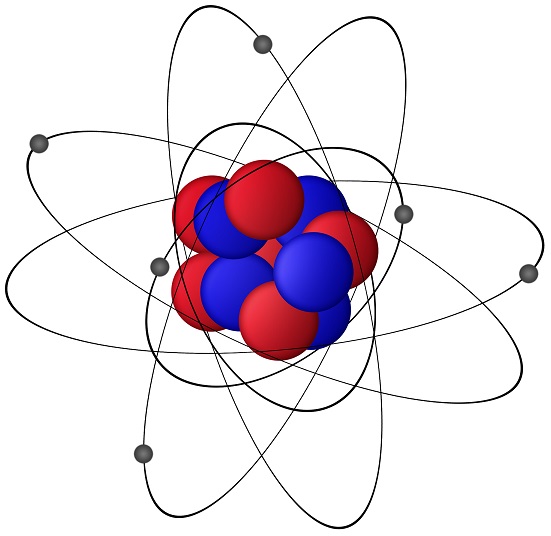
Particles with same charge repel (example: proton and proton) each other, and the particles with opposite charge (example: proton and electron) attract each other.
Two names for different types of charges ("Positive" charge and "Negative" charge) were first assigned around 1750 by Ben Franklin.
An object gains charge when the atoms of that object loss or gain electrons. When an object loses electrons, it becomes positively charged. When object gains electrons, it becomes negatively charged. An atom neutral in charge has equal number of protons and electrons.
What is the SI unit of electric charge?
SI unit for electric charge is coulomb. The SI unit of electric charge coulomb was named in honor of famous French physicist Charles-Augustin de Coulomb.

Electric charge is represented using the letter ’Q’ and electric current is represented by ’I’.
We already know that, current = charge / time (I = Q / t). If we rewrite previous equation, the charge can be defined as electric current multiplied by time.
charge = current * time (Q = I * t).
From above equation, 1 coulomb of electric charge is the electric charge transferred in one second by a steady electric current of one ampere. 1 coulomb of electric charge is equivalent to 6.24 × 1018 elementary charges. Elementary charge is the electric charge carried by a single proton or a single electron.